What can we dig up for you?
Find the nearest location to:
-
Acute Kidney Failure in Cats
Acute renal failure (ARF) or acute kidney failure refers to the sudden failure of the kidneys to perform normal filtration duties. ARF leads to accumulation of toxins and other metabolic wastes in the bloodstream, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and disturbances in the acid-base balance of the blood. The initial prognosis is guarded for all cases of ARF. If the cause is an infection, there is a better prognosis than if the cause is a toxic substance.
Learn More -
Bladder Stones in Cats
Bladder stones are rock-like formations of minerals that develop in the urinary bladder. All stones form because of disease or inflammation in the bladder. The most common signs of bladder stones in the cat are blood in the urine and straining to urinate. Large stones may act almost like a valve, causing an "on-off" or partial obstruction at the neck of the bladder. In males, small stones become lodged in the urethra and cause an obstruction. X-rays (with or without contrast dyes) or ultrasound may be necessary for diagnosis. The fastest way to remove bladder stones is via a surgical procedure called a cystotomy. Special diets or passing a catheter may be successful for some bladder stones. Your veterinarian will advise you of the best course of action for your cat’s particular situation.
Learn More -
Caesarean Sections in Cats - Post Operative Instructions
A caesarean section or C-section is major surgery performed to remove kittens from the uterus. This is most commonly performed as an emergency procedure when there is difficulty with natural birth. Most cats recover quickly from this procedure. Most cats have fully recovered from anesthesia by the time they are discharged to go home.
Learn More -
Corneal Ulcers in Cats
The cornea is the clear, glistening membrane that makes up the surface of the eyeball. A penetration or erosion through a few layers of the outermost corneal epithelium is called a corneal erosion or corneal abrasion. A corneal ulcer is a deeper erosion through the entire epithelium down into the stroma.
Learn More -
Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Disease in Cats
Cystitis is a general term referring to inflammation in the urinary bladder. The term cystitis does not imply a specific underlying cause. In cats, diseases of the lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra) are often grouped under the term feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD). The initial diagnosis of FLUTD is based on the identification of signs of lower urinary tract inflammation.
Learn More -

Emergencies in Cats
Emergencies arise unexpectedly and it is important to stay calm. After realizing what has occurred, it is important to contact your veterinarian for recommendations in order to provide the best chance for a successful outcome. Once you have received initial instructions, it is important to transport your cat to your veterinarian for a complete examination as soon as possible.
Learn More -

First Aid for Cats - Shock, Rescue Breathing and CPR
Medical emergencies occur suddenly and without warning. It is important for all cat owners to have a basic understanding of common veterinary medical emergencies and basic first aid for their pets. This handout provides guidelines you can follow in the event that your cat is experiencing shock and/or requires rescue breathing or CPR. In any emergency situation with your pet, contact your veterinarian or closest emergency facility immediately.
Learn More -

Hepatic Lipidosis in Cats (Fatty Liver Syndrome in Cats)
Hepatic lipidosis, also known as fatty liver syndrome, is unique to cats and is one of the most common liver diseases seen in cats. Usually a cat with hepatic lipidosis has recently gone through a period of anorexia. When fat is broken down rapidly to supply energy and nutrients to the anorectic cat, it can overwhelm the ability of the liver to process and the fat becomes stored in and around the liver cells, further compromising liver function. Diagnosis of hepatic lipidosis is made from blood tests that demonstrate poor liver function and from a liver biopsy or aspirate. This disease is treatable with aggressive nutritional support until a normal appetite returns.
Learn More -
Feline Idiopathic Cystitis
Feline idiopathic cystitis includes a set of clinical signs associated with abnormal urination and is an exclusionary diagnosis. Cats will often suffer waxing and waning of clinical signs such as straining to urinate, blood in urine, and inappropriate urination. Many conditions must be ruled out before a diagnosis of FIC can be made. Treatment involves addressing the stressors that triggered the clinical signs in the first place and improving the cat's environment to reduce or eliminate potential stressors. Pain medications are used to relieve your cat’s discomfort, as well as diet changes to improve clinical signs and reduce the frequency of occurrence.
Learn More -

Fight Wound Infections in Cats
Usually caused by a bite from another cat, fight wound infections can lead to the development of an abscess (a pocket of pus) or cellulitis (pain and swelling in the area of the bite). A cat’s sharp canine teeth can easily puncture the skin of another cat, leaving small, deep, wounds that seal over quickly, so it is important that your cat is seen by a veterinarian for treatment as soon as possible after being bitten.
Learn More -
Frostbite in Cats
Frostbite is the damage that is caused to the skin and other tissues due to extreme cold. The paws, ears and tail are the most common tissues to be affected. Diagnosis is usually based on the cat's medical history and physical examination. If you suspect your cat has frostbite, you should seek medical attention immediately. Mild cases of frostbite usually resolve with little permanent damage while more severe frostbite may result in permanent disfiguration or alteration of the affected tissues. In severe cases, some cats require surgical removal of the necrotic tissue or amputation.
Learn More -
Holiday Safety Tips for Cat Owners
There are many potential hazards that pets face especially during the holidays. With commonsense and planning, exposure to these hazards can be avoided preventing injury or illness. Hazards include tinsel, electrical cords, string from meat, ribbons, Christmas tree water, holiday plants such as mistletoe, holly, and lilies, and food, such as chocolate. Some cats will do better if given a safe space to stay away from company and may require calming remedies to help minimize anxiety and stress during the holidays.
Learn More -
Hypertension or High Blood Pressure in Cats
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, in cats can be a debilitating condition if not treated promptly. Hypertension may be caused by kidney disease, hyperthyroidism, or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Your veterinarian will recommend the best treatment options for your cat based on her specific needs. Prognosis is variable depending on how well these other conditions are controlled.
Learn More -
Icterus (Jaundice) in Cats
Icterus is also known as jaundice is an excessive accumulation of a yellow pigment in the blood and tissues, most easily seen in the gingivae and sclerae. Icterus can be caused by hemolysis, liver disease, or obstruction of the bile duct. Your veterinarian will perform screening tests to determine the root cause of icterus. Based on the preliminary tests, your veterinarian may recommend fine needle aspiration, needle biopsy, or a surgical biopsy. Icterus will resolve once the underlying disease is identified and treated. The prognosis depends on the underlying cause.
Learn More -
Ingestion of Foreign Bodies in Cats
Cats are curious by nature. They love to investigate new sights, smells, and tastes. Unfortunately, this curiosity can lead them into trouble. Cats are notorious for ingesting thread, wool, paper, rubber bands, plant materials, and small toys. Not all foreign objects pass through the digestive tract without complication.
Learn More -

Ethylene Glycol Poisoning in Dogs
Ethylene glycol, a sweet-tasting, odorless liquid, is the active ingredient in antifreeze. Ethylene glycol can also be found, in lower concentrations, in some windshield de-icing agents, hydraulic brake fluid, motor oils, solvents, paints, film processing solutions, wood stains, inks, printer cartridges, etc.
Learn More -
Pancreatitis in Cats
The pancreas is a vital organ on the right side of the abdomen adjacent to the stomach. It produces enzymes to assist in food digestion and hormones such as insulin, which regulates blood sugar or glucose metabolism. When the pancreas becomes inflamed, the condition is called pancreatitis. Common clinical signs include decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. If the attack is severe, acute shock or death may occur. Successful pancreatitis management will depend on early diagnosis and prompt medical therapy.
Learn More -
Pleural Effusion in Cats
Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity. The fluid is not found within the lungs, but instead within the pleural sac, essentially meaning the lungs are floating in a chest that is full of fluid. Several conditions can cause pleural effusion, including chylothorax, heart failure, and tumors in the lungs or chest wall. Immediate treatment often requires oxygen support and the removal of the excess fluid by thoracocentesis, which can also then be tested to diagnose the cause of the pleural effusion. Treatment and prognosis vary depending on the underlying cause of the pleural effusion.
Learn More -
Pyometra in Cats
Pyometra is defined as an infection in the uterus. Pyometra is considered a serious and life threatening condition that must be treated quickly and aggressively. Pyometra may occur in any sexually intact young to middle-aged cat; however, it is most common in older cats. Typically, the cat has been in heat within the previous 4 weeks.
Learn More -
Pyothorax in Cats
Pyothorax is the presence of inflammatory fluid or pus within the chest cavity, which is the area between the lungs and the inner walls of the ribs. Signs of pyothorax include rapid, shallow, open-mouthed breathing that may be painful, depression, lethargy, decreased appetite. Clinical examination by a veterinarian, particularly listening to the chest with a stethoscope, may indicate fluid in the chest.
Learn More -
Seizures and Epilepsy in Cats
A seizure is a sudden surge in the electrical activity of the brain causing signs such as twitching, shaking, tremors, convulsions, and/or spasms. Epilepsy is used to describe repeated episodes of seizures. With epilepsy, the seizures can be single or may occur in clusters, and they can be infrequent and unpredictable or may occur at regular intervals. Since many different diseases can lead to seizures, it is important to perform diagnostic tests to investigate the underlying cause of the seizures. Treatment of seizures in the cat depends on the nature of the underlying disease.
Learn More -
Pancreatitis in Cats - Pancreas-Specific Lipase
Pancreas-specific lipase is a form of lipase produced only in the pancreas and is highly specific to the pancreas. Blood values increase only when there is pancreatic inflammation. There is now a version of the fPLI test that can be used in-clinic (SNAP fPL© from IDEXX). Ideally, the sample should also be sent to the laboratory to get an actual value of fPLI to help with treatment and monitoring.
Learn More -
Pancreatitis in Dogs - Pancreas-Specific Lipase
Pancreas-specific lipase is a form of lipase produced only in the pancreas and is highly specific to the pancreas. Blood values increase only when there is pancreatic inflammation. A version of the cPLI test can now be used in-clinic (SNAP fPL© from IDEXX). Ideally, the sample should also be sent to the laboratory to get an actual value of cPLI to help with treatment and monitoring.
Learn More -

Household Hazards - Toxic Hazards for Cats
Many think that because cats are finicky eaters they are poisoned less often than dogs. However, with their curiosity and fastidious grooming, intoxication is, unfortunately, not uncommon. Several factors predispose cats to becoming ill once they have been exposed to even a small amount of a poisonous substance.
Learn More -

Vomiting in Cats
Vomiting may be caused by disorders of the stomach, but is a clinical sign that can occur with many diseases and problems. Different types of vomiting are reviewed. Any required tests are determined based on physical examination of your cat and questions regarding how your cat has been acting and feeling at home.
Learn More -

Anaphylaxis in Dogs
Anaphylaxis is an acute severe allergic reaction caused by an overreaction of the body’s immune system to an allergen such as a food protein, medication, vaccine antigen or other chemical. The most common signs include itching, cutaneous edema, hives, excessive drool, vomiting, diarrhea or respiratory distress. Diagnosis is made based on history and physical exam.
Learn More -
Bladder Stones in Dogs
Bladder stones are rock-like formations of minerals that develop in the urinary bladder. The most common signs that a dog has bladder stones are hematuria and dysuria. Bladder stones can develop within a few weeks or they may take months to form. Most bladder stones are visible on radiographs or an ultrasonic bladder examination. There are three main treatment options for bladder stones: 1) surgical removal; 2) non-surgical removal by urohydropropulsion, or 3) dietary dissolution. Prevention is possible in some cases, depending on the chemical composition of the stones.
Learn More -

Bloat: Gastric Dilatation and Volvulus in Dogs
Gastric Dilatation and Volvulus (GDV) is an acute life-threatening condition where the stomach fills with large amounts of air and then twists around effectively cutting off the outputs to the esophagus and intestine. It then continues to expand putting pressure on the mucosa, major vessels and diaphragm. Because of the constriction of major vessels returning to the heart the dog will collapse from lack of oxygen and nutrients to vital organs. Underlying causes are still a mystery but most dogs affected are large breed, deep chested male dogs although any dog can experience GDV. There is a definite risk in dogs that have eaten large meals and then exercise. Bloat may be diagnosed by physical exam but radiographs and other testing is needed to show volvulus. Treatment involves decompressing the stomach with a stomach tube or a percutaneous catheter, shock treatment with IV fluids and emergency medications, surgery to correct the volvulus and identify and remove any necrotic areas of stomach or spleen. Mortality rate ranges from 15-40% in treated cases. There is no guaranteed prevention for GDV but gastropexy can reduce the risk. Attention to diet, feeding and exercise may also prevent gastric dilation.
Learn More -
Cataracts in Dogs
Inside the eye is a lens that focuses light on the back of the eye, or retina. Vision occurs at the retina. The structure of the eye is similar to a camera, which has a lens to focus light on the film. A cloudy or opaque lens is called a cataract.
Learn More -
Cervical Stenosis (Wobbler Syndrome) in Dogs
Cervical stenosis is caused by compression of the spinal cord, usually at the base of the neck. Although the spinal cord compression occurs in the neck, the hind legs are often affected first. In severe cases, the dog may suddenly develop total paralysis of all four limbs. The condition is most prevalent in Great Danes and Doberman Pinschers. It is diagnosed by myelography, CT scans, or MRI. Anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics may relieve the initial discomfort, but the greatest chance of success lies with surgery. Most pets enjoy a relatively normal lifestyle following surgery.
Learn More -

Caesarean Sections in Dogs - Post-Operative Instructions
A caesarean section is a major surgery usually performed in an emergency to help deliver puppies. As with any anesthesia, the dog may be sleepy but should be able to eat a high quality diet and nurse puppies within a few hours. The dog should be monitored for fever, abnormal vulvar discharge, and abnormalities at her incision. It is important to ensure that puppies are able to nurse well. If not, or if the dog can not produce enough milk, then commercial milk replacer is recommended. Colostrum ingestion is important for immune protection. If puppies are not nursing within the first 24 hours, then they will need additional veterinary care. Ambient temperature is important in the first 2-4 weeks after birth as puppies cannot regulate their temperature well.
Learn More -

Chocolate Poisoning in Dogs
Chocolate is toxic to dogs. While rarely fatal, chocolate ingestion often results in significant illness. Chocolate is toxic because it contains the alkaloid theobromine. Theobromine is similar to caffeine and is used medicinally as a diuretic, heart stimulant, blood vessel dilator, and a smooth muscle relaxant.
Learn More -
Corneal Ulcers in Dogs
The cornea is the transparent, shiny membrane that makes up the front of the eyeball. With a corneal ulcer, fluid is absorbed from the tears into the stroma, giving a cloudy appearance to the eye. The most common cause of a corneal ulcer is trauma. Less common causes of corneal ulcers include bacterial infections, viral infections, and other diseases.
Learn More -
Hives (Urticaria) in Dogs
Urticaria or hives is a skin condition characterized by raised red skin welts and is caused by an allergic reaction. These swollen welts can appear anywhere on the body, including the face, lips, tongue, throat, and ears. Urticaria is generally caused by direct contact with a substance that causes an allergic reaction. Most cases of urticaria are self-limiting and cause no significant health threat to your pet. Antihistamines and corticosteroids by injection usually bring about a dramatic improvement, sometimes in as little as a few minutes.
Learn More -
Uveitis in Dogs
Uveitis is an inflammation of one or more of the structures making up the uvea. Signs of uveitis are severe pain with an intense reddening of the visible parts of the eye. Measurement of intraocular pressure is often performed to diagnose uveitis. Treatment involves reducing the pain and inflammation in the eye as well as treating the initial cause of the disease.
Learn More -
Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Treatment in Dogs
Diabetes mellitus results from an inadequate production of insulin from the pancreas. The primary treatment is replacement by insulin injections. The body’s response to the injections needs to be regularly monitored by glucose curves over 12-24 hours. There are several glucometers that can be used at home for this purpose. Insulin must be stored and reconstituted carefully to ensure dosing is accurate. Giving subcutaneous injections of insulin can seem daunting at first, but by following the directions in this handout, it will quickly become second nature to both you and your pet. Hypoglycemia can result from too much insulin, not enough food, or excess exercise. Pet owners are trained to recognized hypoglycemia and treat or obtain emergency veterinary attention.
Learn More -

Emergencies in Dogs
Emergencies arise unexpectedly and it is important to stay calm. After realizing what has occurred, it is important to contact your veterinarian for recommendations in order to provide the best chance for a successful outcome. Once you have received initial instructions, it is important to transport your dog to your veterinarian for a complete examination as soon as possible.
Learn More -
Epilepsy in Dogs
Epileptic seizures in pets are a diagnosis of exclusion and may be found in any dog but there may be some breed predispositions that are more common. The cause is often unknown. A variety of medications are available to help control the seizure activity if an underlying cause is not found.
Learn More -

Fading Puppy Syndrome in Dogs
Fading puppy syndrome describes puppies that decline in health and die within about two weeks of birth. Neonatal puppies are fragile and so there can be many causes of this syndrome including birth defects, inadequate care from the mother, poor health status of the mother and/or infectious diseases. As well as addressing a specific cause, treatment focuses on maintaining hydration and warmth while providing adequate nutrition. Environmental hygiene is extremely important.
Learn More -

First Aid for Dogs
Emergencies arise unexpectedly and it is important to stay calm. After realizing what has occurred, it is important to contact your veterinarian in order to provide the best chance for a successful outcome. Basic first aid in the meantime can help reduce the chance for complications.
Learn More -
Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome in Dogs (Hemorrhagic Gastroenteritis)
Acute hemorrhagic gastroenteritis (AHDS) (also known as hemorrhagic gastroenteritis [HGE]), is an acute disorder of dogs characterized by vomiting and bloody diarrhea. AHDS can affect any breed, age, size, or gender of dog, but it is most common in small- and toy-breed dogs. The exact cause of AHDS remains unknown. An elevated hematocrit in combination with a low or normal total protein is an important clue that a dog may have AHDS. Intravenous fluid therapy with potassium and electrolyte supplementation provides the foundation of AHDS therapy. Dogs with AHDS may die, if left untreated.
Learn More -

Congestive Heart Failure in Dogs
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a term that refers to the heart's inability to pump adequate blood to the body. There are many causes of CHF in dogs. The two most common causes are mitral valve insufficiency (MVI), or a leaky mitral valve, the valve between the left atrium and the let ventricle and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
Learn More -
Heat Stroke in Dogs
Heatstroke is another term for hyperthermia. Dogs suffering from heatstroke can have varied signs from high respiratory rate to coma depending on how high their temperature is. Heat stroke is most often caused by a dog being left in a car without adequate ventilation; however, it can happen outside as well if the dog does not have access to shade or water. Dogs have difficulty with heat exchange as they only have a few sweat glands in their feet and mainly control heat exchange by panting. Because of this, brachycephalic dogs or muzzled dogs are at higher risk. Treatment for heat stroke requires controlled evaporative cooling with water and fans, intravenous fluids, sedation, and oxygen therapy. It is important to discontinue active cooling once the body temperature reaches 103°F or the dog can quickly become hypothermic. Prognosis depends on the extent and duration of temperature elevation. Some dogs recover normally but more severe cases will have permanent organ damage or may die from hyperthermia.
Learn More -
Anorexia and Lethargy in Birds
Anorexia (a loss of appetite) and lethargy (a feeling of listlessness and general inactivity) are commonly seen in sick pet birds. While not diagnostic for any specific disease, these signs can indicate severe illness in a bird that requires immediate medical attention. Birds rarely get sick overnight. Usually birds are ill before pet owners notice outward signs of illness.
Learn More -
Icterus (Jaundice) in Dogs
Icterus is also known as jaundice is an excessive accumulation of a yellow pigment in the blood and tissues, most easily seen in the gingivae and sclerae. Icterus can be caused by hemolysis, liver disease, or obstruction of the bile duct. Your veterinarian will perform screening tests to determine the root cause of icterus. Based on preliminary tests, your veterinarian may recommend fine needle aspiration, needle biopsy, or a surgical biopsy. Icterus will resolve once the underlying disease is identified and treated. The prognosis depends on the underlying cause.
Learn More -
Insect Bite Reaction in Dogs
Bee stings and bites from spiders, fleas, and ticks are the most common causes of insect bite reactions in pets. Insect bites can cause mild to severe allergic reactions in many dogs. Fortunately, most reactions are minor and have an excellent prognosis for recovery. Treatment typically involves antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Learn More -

Egg Binding in Birds
Egg binding is not uncommon in birds and may be resolved easily if treated early. Egg binding occurs when the female bird is unable to expel the egg from her body. If a prolonged period has elapsed since the bird began attempting to lay the egg, she may become critically ill. Birds with egg binding may or may not have passed an egg more than 2 days ago, are usually weak, not perching, often sitting low on the perch or on the bottom of the cage, and are straining as if trying to defecate or to lay an egg. Treatment varies depending upon how sick the bird is, as well as the location of the egg and the length of time the bird has been egg bound. Critically ill birds are first treated supportively for shock, and then attempts are made to extract the egg. If your veterinarian cannot see the egg through the vent, surgery under general anesthetic may be necessary to remove the egg from the abdomen. A hysterectomy (removal of the oviduct and uterus) is typically the last choice therapy, when medical and egg extraction through the vent are not possible.
Learn More -

Caring for Orphaned Puppies
Raising orphan puppies requires great care, time, and vigilance. Puppies must be kept at appropriate temperatures and humidity levels. Hypoglycemia can develop quickly if they are not ingesting food regularly. Orphaned puppies need to be fed appropriate amounts of a commercial puppy milk replacer at regular intervals and can be fed by bottle or feeding tube. After each feeding the puppies will need to be stimulated to urinate and defecate. Around 4 weeks, puppies can start the weaning process onto puppy food by mixing puppy food with the commercial milk replacer to make a gruel-type food. Orphaned puppies need to be dewormed every 2 weeks starting at 2 weeks of age and should start their vaccination series no later than 6 weeks. A veterinarian should be consulted early and frequently throughout the first 6-8 weeks of life.
Learn More -
Household Hazards and Dangers to Birds
Birds are naturally mischievous and if not properly supervised, will get into many predicaments. It is crucial that you bird proof your home. The bird's cage is its house and the confines of your home represent the bird's environment.
Learn More -

Pyometra in Dogs
Pyometra is defined as an infection in the uterus. Pyometra is considered a serious and life threatening condition that must be treated quickly and aggressively. The preferred treatment is to surgically remove the infected uterus and ovaries. Another approach to treating pyometra is the administration of prostaglandins, although the success rate is highly variable.
Learn More -

Recognizing the Signs of Illness in Pet Birds
In the wild, a bird will endeavor to uphold a strong appearance when sick. This is called, survival of the fittest. By the time a pet bird actually shows an owner that it is unwell, it has likely been sick for some time. Many things contribute to ill health. This handout provides bird owners a categorized list of signs that should alert them that their bird is sick.
Learn More -
Seizures in Birds
Seizures are reasonably common in pet birds and should be treated as a medical emergency. Species that are often affected include Amazon parrots, African grey parrots, budgies, canaries, cockatiels, finches, and lovebirds. There are several possible causes of seizures in birds. Diagnostic testing is often required so that your veterinarian can diagnose the problem and determine the necessary treatment plan.
Learn More -

Testing and Diagnostics for Sick Pet Birds
Wellness testing, performed routinely on apparently healthy birds, screens for underlying, inapparent problems. Veterinarians also use test results in conjunction with physical examination findings and the owner’s account of the bird’s history to diagnose illnesses. Blood tests include the complete blood count and chemistry profile. Other tests your veterinarian may use to assess your bird’s health and diagnose disease include Gram’s stain, culture and sensitivity testing, parasitology, X-rays, laparoscopic surgery, cytology, histopathology, virology, and genetic (PCR) testing. Post-mortem examination after a bird dies may be recommended to determine the cause of death.
Learn More -

Plants That are Toxic to Birds
Many birds naturally eat plants as part of their diet. Some birds will chew on and possibly consume plants out of curiosity or during play. Many toxic plants will just make a bird sick if they ingest them, but some can kill them. Fortunately, rather than ingesting plants, most birds shred and play with plants with which they come in contact. This handout catalogues many of the indoor and outdoor plants that are considered to be potentially toxic to birds.
Learn More -
Strokes in Dogs
Strokes are rare in dogs. Some common causes include a blood clot such as a thrombus or embolus that lodges in a cerebral blood vessel, or cerebral bleeding from trauma or as a result of thrombocytopenia; however, the cause is often unknown. Signs of a stroke are variable depending on the region or regions of the brain affected, and the degree and duration of blood and oxygen deprivation. Magnetic resonance imaging is the ideal diagnostic test for diagnosing a stroke. Treatment is quite complex and there is no guarantee of complete success. Your veterinarian will help you assess progress and plan remedial action.
Learn More -
Blood Feathers in Birds
Blood feathers are a normal maturation process for all feathers on birds. When feathers first erupt from the skin they contain blood. Injury to the feather as it grows may cause the blood feather to become broken causing blood loss that at times may require emergency treatment by an avian veterinarian.
Learn More -
Chinchillas - Health Conditions
Chinchillas are generally hardy animals but are susceptible to several unique health conditions; understanding them will help you care for your pet and manage potential health problems. This handout describes the most common conditions seen in pet chinchillas.
Learn More -
Ferrets - Problems
Ferrets have several unique problems; understanding these problems will allow you to better care for your pet and minimize future health care problems.
Learn More -
Reproductive Diseases in Ferrets
Reproductive disease in ferrets is rare today, as most pet ferrets are spayed or neutered at a young age. One disease that is still occasionally seen in pet ferrets occurs in females that are not spayed. This is called hyperestrogenemia and is a result of persistently high blood levels of estrogen in unspayed females that are not bred or fails to ovulate.
Learn More -
Iguanas - Problems
Iguanas have several unique disease problems; understanding these problems will allow you to better care for your pet and minimize future health care problems.
Learn More -
Frostbite in Dogs
Frostbite is the damage that is caused to the skin and other tissues due to extreme cold. The paws, ears, and tail are the most common tissues to be affected. Diagnosis is usually based on the dog's medical history and physical examination. If you suspect your dog has frostbite, you should seek medical attention immediately. Mild cases of frostbite usually resolve with little permanent damage, while more severe frostbite may result in permanent disfiguration or alteration of the affected tissues. In severe cases, some dogs require surgical removal of the necrotic tissue or amputation.
Learn More -

Holiday Safety Tips for Dog Owners
There are many potential hazards that pets face especially during the holidays. With commonsense and planning exposure to these hazards can be avoided preventing or illness. Hazards include tinsel, electrical cords, string from meat, ribbons, Christmas tree water, holiday plants such as mistletoe, holly, and lilies, and foods such as chocolate and other human foods including bread dough. Some dogs will do better if given a safe space to stay away from company and may require calming remedies to help minimize anxiety and stress during the holidays.
Learn More -
Ingestion of Foreign Bodies in Dogs
One of the more common and potentially life-threatening conditions seen in veterinary practice is foreign body obstruction. Some foreign bodies pass through the intestinal tract, but if an obstruction occurs, surgical removal of the blocked object is the only treatment. Clinical signs may include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and lethargy. X-rays are typically performed to diagnose foreign bodies. The prognosis is variable depending upon multiple factors.
Learn More -
Health Problems in Rodents
Rodents commonly develop certain health problems. Rabies is very unlikely in pet rodents (especially those housed inside, away from other animals). Many rodents barber their own hair or the hair of a cagemate as a result of stress in the form of overcrowding, fighting, or boredom. Foot necrosis is caused by fine fiber or thread nesting material wrapping around toes or feet and cutting off circulation. Guinea pigs cannot make their own vitamin C, so they must receive it as a supplement in their diets. All pet rodents, but especially guinea pigs and chinchillas, are very susceptible to life-threatening heat stroke from high ambient temperatures (greater than 80°F or 27°C). Certain antibiotics should never be used in rodents, as they upset the normal bacteria that live in rodents’ gastrointestinal tracts and favor toxin-producing bacteria that can be fatal to rodents. Chromodacryorrhea is seen in mice, gerbils, and most often in rats Diarrhea can have several different causes in rodents including infections with different bacteria, parasites, or viruses. Rodents also commonly get fractured bones from mishandling or falls, bacterial skin infections (dermatitis) on their faces, and may also experience seizures.
Learn More -
Reptiles: Dystocia
Abdominal swelling in any reptile is always a concern that needs to be brought to the attention of a veterinarian well versed in reptile medicine. In female reptiles, this swelling often means that the individual has eggs or fetus that are ready to be delivered. When the female cannot deliver the eggs or babies, this is referred to as dystocia. This condition can be life threatening and need attention ASAP.
Learn More -
Eye Emergencies in Horses
Injuries to the eye and surrounding areas of the head and face are relatively common in horses and ponies due to their inquisitive nature and as a result of 'arguments' with each other and with structures such as stable doors, fence posts, trees, etc.
Learn More -
Fractures in Horses
A fracture is a crack or break in a bone. Just about every bone in the body can be fractured but fractures of the bones of the limbs are of major importance in horses and ponies.
Learn More -
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Cats
AIHA or IMHA is a life-threatening condition which may occur as a primary condition or secondary to another disease. Most cats with AIHA have severe anemia, their gums will be very pale, they will be listless and tire more easily, be anorexic and will have increased heart and respiration rates. Diagnosis involves CBC, biochemical profiles, urinalysis, and X-rays or ultrasound of the abdomen and chest. Treatment may involve blood transfusions and other medications over a prolonged course of time. The prognosis may be better if an underlying cause can be identified.
Learn More -
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Dogs
AIHA or IMHA is a life-threatening condition which may occur as a primary condition or secondary to another disease. Most dogs with AIHA have severe anemia, their gums will be very pale, they will be listless and tire more easily, be anorexic and will have increased heart and respiration rates. Diagnosis involves CBC, biochemical profiles, urinalysis, and X-rays or ultrasound of the abdomen and chest. Treatment may involve blood transfusions and other medications over a prolonged course of time. The prognosis may be better if an underlying cause can be identified.
Learn More -
Skunk Spray and Your Dog
Skunks spray volatile compounds from their anal sacs if they feel threatened by a potential predator such as a dog. Dogs can come across a skunk in rural or urban areas but most often at dawn or dusk and in areas where skunks make their den. Avoiding these areas at these times is the best way to avoid a skunk encounter. If sprayed in the face your dog may need veterinary care, as corneal damage can occur if sprayed in the eyes, and vomiting, diarrhea, or anemia can result if sprayed in the mouth. Washing the offending oils from the dog is complicated, but there are several commercial skunk shampoos that are good for this. If these are not available a combination of hydrogen peroxide, baking soda, and dish soap can be used to help in the short term. It is important to avoid getting this solution in the eyes or mouth as the ingredients can be irritating and create more problems. Skunks may carry rabies so avoid contact between them and your dog.
Learn More -
Xylitol Poisoning in Dogs
Xylitol is a naturally occurring substance that is widely used as a sugar substitute. Chemically, it is a sugar alcohol, and found naturally in berries, plums, corn, oats, mushrooms, lettuce, trees, and some other fruits.
Learn More -

Bite Wounds in Dogs
Bite wounds are a common injury veterinarians see. If left alone, wounds have the potential to become more complicated, as they are likely infected and delaying treatment only makes it worse. Antibiotics, pain medications, and stitches may all be involved in the post-bite wound care.
Learn More -
Urate Bladder Stones in Dogs
Urate bladder stones are most commonly the result of a genetic abnormality seen in breeds such as Dalmatians. Other causes of urate bladder stones include liver diseases such as portosystemic shunts. The most common signs that a dog has bladder stones are hematuria and dysuria. There are two primary treatment strategies for treating urate bladder stones in dogs: non-surgical removal by urohydropropulsion, and surgical removal. Dogs that have experienced urate bladder stones will often be fed a therapeutic diet for life. Dogs with liver disease will need to be treated appropriately prior to addressing urate bladder stone management.
Learn More -
Struvite Bladder Stones in Dogs
One of the more common bladder stones found in dogs is composed of magnesium ammonium phosphate hexahydrate (also known as struvite stones). Struvite bladder stones usually form as a complication of a bladder infection caused by bacteria, and if the urine becomes exceptionally concentrated and acidic. The most common signs that a dog has bladder stones are hematuria and dysuria. There are three primary treatment strategies for struvite bladder stones: 1) feeding a special diet to dissolve the stone(s), 2) non-surgical removal by urohydropropulsion and 3) surgical removal. Dogs that have experienced struvite bladder stones will often be fed a therapeutic diet for life.
Learn More -
Cystine Bladder Stones in Dogs
Cystine bladder stones appear to be the result of a genetic abnormality that prevents a dog from reabsorbing cystine from the kidneys. While bladder stones in general are somewhat common in dogs, cystine bladder stones are rare. Your veterinarian may be able to palpate the stones or may need to perform imaging studies such as a bladder ultrasound or a contrast radiographic study. There are two primary treatment strategies for treating cystine bladder stones in dogs: urohydropropulsion or surgical removal. Dogs that have developed cystine bladder stones in the past will often be fed a therapeutic diet for life. Unfortunately, cystine stones have a high rate of recurrence, despite careful attention to diet and lifestyle.
Learn More -
Calcium Oxalate Bladder Stones in Dogs
One of the more common uroliths in the dog is composed of calcium oxalate crystals. Current research indicates that urine high in calcium, citrates, or oxalates and is acidic predisposes a pet to developing calcium oxalate urinary crystals and stones. The most common signs that a dog has bladder stones are hematuria and dysuria. The only way to be sure that a bladder stone is made of calcium oxalate is to have the stone analyzed at a veterinary referral laboratory. Unfortunately, calcium oxalate stones have a somewhat high rate of recurrence, despite careful attention to diet and lifestyle.
Learn More -

Eclampsia in Cats
Eclampsia is essentially hypocalcemia in a cat who has recently given birth. It can quickly progress from weakness to tremors, seizures, or paralysis. Treatment involves immediate intravenous injections of calcium and other drugs. Recovery from eclampsia is usually rapid and complete if treated early. Fortunately, it is uncommon in cats.
Learn More -
Eclampsia in Dogs
Eclampsia is hypocalcemia in a dog who has recently given birth. Breeds such as Chihuahuas, Pomeranians, Toy Poodles, Miniature Pinscher, Shih Tzu, and other small breeds are at an increased risk. Eclampsia is considered an emergency and immediate medical attention should be sought. It can quickly progress from weakness to tremors, seizures, or paralysis. Treatment involves immediate intravenous injections of calcium and other drugs. Recovery from eclampsia is usually rapid and complete if treated early.
Learn More -

Penetrating Trauma and Gunshot Wounds
Penetrating wounds such as sticks, arrows, or gunshots can be life-threatening though the outer appearance of a wound may not seem as severe. Take immediate steps to calm your pet, stabilize any foreign body that is present, and get your pet to your veterinarian. Surgery may be necessary after your pet is stabilized.
Learn More -

Paint and Varnish Poison Alert for Dogs and Cats
House paint, art paint, varnishes and other decorative or protective solvents come in many varieties… and most are dangerous to dogs and cats. Water-based paints, the most common, include latex, tempera, and poster paints.
Learn More -

Zinc Poisoning in Pets
Pets and people need some zinc in their diets. However, too much zinc can cause serious health problems.
Learn More -

Chemotherapy Drug Poisoning in Dogs and Cats
Chemotherapy drugs are used to treat cancer and other conditions in people because they target and kill rapidly dividing neoplastic (cancer) cells and other cells. They are primarily used as anti-cancer agents but may also provide benefits for a variety of auto-immune disorders and organ transplant recipients as immunosuppressive agents.
Learn More -
Anorexia in Dogs
A dog that is not wanting to eat or is not eating, is a dog who has a potentially life-threatening medical condition. Many conditions can lead to the inability of your dog to eat or for your dog to lose his appetite completely. It is important to find the underlying cause so that an appropriate treatment plan can be created. Appetite stimulants may be prescribed and in some cases a feeding tube may be placed by your veterinarian. Decreased food intake or any change in eating habits warrants investigation by your veterinarian.
Learn More -
Anorexia in Cats
A cat that is not wanting to eat or is not eating, is a cat who has a potentially life-threatening medical condition. Many conditions can lead to the inability of your cat to eat or for your cat to lose her appetite completely. It is important to find the underlying cause so that an appropriate treatment plan can be created. Appetite stimulants may be prescribed and in some cases a feeding tube may be placed by your veterinarian. Decreased food intake or any change in eating habits warrants investigation by your veterinarian.
Learn More -

Ethylene Glycol Poisoning in Cats
Ethylene glycol, a sweet-tasting, odorless liquid, is the active ingredient in antifreeze. Ethylene glycol can also be found, in lower concentrations, in some windshield de-icing agents, hydraulic brake fluid, motor oils, solvents, paints, film processing solutions, wood stains, inks, printer cartridges, etc.
Learn More -
Essential Oil and Liquid Potpourri Poisoning in Cats
Many liquid potpourri products and essential oils, including oil of cinnamon, citrus, pennyroyal, peppermint, pine, sweet birch, tea tree (melaleuca), wintergreen, and ylang ylang, are poisonous to cats. Both ingestion and skin exposure can be toxic.
Learn More -

Mothball Poisoning in Cats
Mothballs are solid pesticides that slowly release a vapor to kill and repel moths, their larvae, and other insects from stored clothing and fabric. Mothballs are sometimes also used to repel snakes, mice, and other animals, although this use is not recommended and can be harmful to pets, children, and the environment.
Learn More -
First Aid for Tail Injuries in Dogs
Tail injuries are common and can sometimes be managed with home first aid but some cases require veterinary care. Abrasions are mild scrapes that can be treated with daily cleaning and application of antibiotic ointment. Lacerations are more serious cuts that may expose underlying muscle and bone requiring stitches and often antibiotics. Happy tail is a condition where the skin at the end of the tail becomes damaged and continues to split and bleed whenever the wagging tail hits a hard surface. Bandaging, antibiotics and pain medication may help these heal but amputation may become necessary to reduce re-injury. Tail fractures can heal well if they occur near the tip of the tail but if bones are severely damaged then amputation may be required. Nerve damage can occur from fractures, crushing injuries or severe tail pulls causing stretching or tearing of the nerves and can result in loss of fecal and urinary continence and can also result in a limp tail. Limber tail is a painful muscle condition likely caused by overexertion and treated with rest and anti-inflammatories.
Learn More -

Pyrethrin/Pyrethroid Poisoning in Cats
Pyrethrin insecticides are naturally derived from the chrysanthemum (mum) flower, and pyrethroids are the synthetic versions. The formulations of these products vary in concentration, synergists, and carriers depending on their intended use.
Learn More -
First Aid for Broken Nails in Dogs
Broken nails are acute painful injuries that require first aid, and in some cases, a veterinary visit. Nails are made up of a collection of blood vessels and nerves covered by a hard protective layer of keratin. Bleeding should initially be controlled with pressure from gauze or a towel, followed by cauterizing powder if needed. Any remaining damaged part needs to be removed which usually requires veterinary care. Depending on the level of the break, your dog may need to be sedated and/or the area numbed with a nerve block prior to trimming the nail above the break. Depending on the severity, a bandage may be placed to protect the injury. Antibiotics and pain medications may be prescribed if indicated. Broken nails are best prevented by keeping all nails short through regular trimmings.
Learn More -
First Aid for Insect Stings in Dogs
Insect stings or bites can cause mild signs of swelling, pain, and itching or can be more severe causing hives, anaphylactic reactions, difficulty breathing, vomiting, diarrhea, or seizures. If the sting or bite has been observed, look for the insect or spider to allow identification. Look for a stinger and carefully remove it without squeezing more venom out of the venom sac. Depending on the severity of the reaction, first aid including cool packing the area, dosing with oral antihistamine, and prevention of self-trauma may be all that is needed; however, in more severe cases emergency veterinary attention is required to stabilize the dog, screen for organ dysfunction, and provide supportive care.
Learn More -

First Aid for Falls in Dogs
Dogs that fall from heights can suffer sprains, broken bones, head trauma, and chest or abdominal injuries. Small dogs can incur the same degree of injury falling from much smaller distances. Toy breeds have been known to break one or both legs when simply jumping down from the sofa.
Learn More -

First Aid for Limping Dogs
Although most limps need veterinary attention, there are a few first aid measures you can perform at home if your dog is hobbling around.
Learn More -

First Aid for Bleeding in Dogs
When it comes to bleeding, what you can't see can be more serious than what you can. To minimize blood loss, you can provide first aid for bleeding dogs until you arrive at the veterinarian.
Learn More -

Aortic Thromboembolism in Dogs
An aortic thromboembolism results when a blood clot is dislodged and travels through the aorta, becoming lodged in a distant location. This causes severely reduced blood flow to the tissues receiving blood from that particular part of the aorta, leading to decreased oxygen in the tissues. Aortic thromboembolism is a rare occurrence in dogs and can be associated with can be associated with endocarditis, cancer, sepsis, hyperadrenocorticism, and with increased protein-loss through diseased kidneys. Sudden paralysis and pain, usually in the rear legs, are the most common clinical signs of aortic thromboembolism, although weakness and lameness may be seen. Initially, dogs may need to be treated as inpatients. Drugs to prevent platelets from clumping together will be prescribed. The expected course of this disorder is days to weeks for full recovery of function to the legs, but the prognosis in general is very poor.
Learn More -
Pulmonary Thromboembolism (Blood Clots in the Lungs) in Dogs
Pulmonary thromboembolism describes a condition when a blood clot lodges in one of the pulmonary arteries, blocking blood flow into the portion of the lung served by that artery. The signs of pulmonary thromboembolism include very sudden difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, decreased appetite, fainting, coughing, spitting up blood, weakness, exercise intolerance, and the inability to get comfortable. There are many important considerations and potential causes of pulmonary thromboembolism in dogs. Many dogs with thromboembolism are first treated as inpatients until the oxygen levels in their blood returns to normal. Once the dog returns home, it is important to restrict activity. There are some medications available for treating this disorder in dogs. The prognosis for dogs with pulmonary thromboembolism is generally guarded to poor, and it depends upon resolution of the underlying cause.
Learn More -
Brain Injury in Dogs
Brain injuries are devastating and, unfortunately, often fatal. The typical signs of brain injury in a dog include altered consciousness that may signal bleeding in the skull, decreased blood flow to the brain, or fluid causing swelling within the brain itself. There are many potential causes of brain injury and treatment will always be determined by the underlying problem that led to the injury.
Learn More -

Cyanosis in Dogs
Cyanosis is defined as a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes of the body caused by inadequate oxygen levels. Several different conditions involving the cardiovascular/circulatory system and/or the respiratory system that can lead to cyanosis, including congenital defects, degeneration of heart valves or heart muscle, blood clots in the lungs, pulmonary hypertension, pneumonia, asthma, lung flukes, smoke inhalation, or muscle damage to the diaphragm. Cyanosis is an emergency, and the root cause may be life-threatening and may or may not be reversible. Once back home, homecare instructions must be followed carefully.
Learn More -
First Aid for Bleeding Cats
When it comes to bleeding, what you can't see can be more serious than what you can see. Visible bleeding from a broken nail or cut ear looks scary and makes a terrible mess, but internal bleeding in the chest or abdomen that you can't see is much more dangerous.
Learn More -
Cyanosis in Cats
Cyanosis is defined as a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes of the body caused by inadequate oxygen levels. Several different conditions involving the cardiovascular/circulatory system and/or the respiratory system that can lead to cyanosis, including congenital defects, degeneration of heart valves or heart muscle, blood clots in the lungs, pulmonary hypertension, pneumonia, asthma, lung flukes, smoke inhalation, or muscle damage to the diaphragm. Cyanosis is an emergency, and the root cause may be life threatening and may or may not be reversible. Once back home, homecare instructions must be followed carefully.
Learn More -
Brain Injury in Cats
Brain injuries are devastating and, unfortunately, often fatal. The typical signs of brain injury in a cat include altered consciousness that may signal bleeding in the skull, decreased blood flow to the brain, or fluid causing swelling within the brain itself. There are many potential causes of brain injury and treatment will always be determined by the underlying problem that led to the injury.
Learn More -
First Aid for Broken Nails in Cats
Broken nails are acute painful injuries that require first aid, and in some cases, a veterinary visit. Nails are made up of a collection of blood vessels and nerves covered by a hard protective layer of keratin. Bleeding should initially be controlled with pressure from gauze or a towel, followed by cauterizing powder if needed. Any remaining damaged part needs to be removed which usually requires veterinary care. Depending on the level of the break, your cat may need to be sedated and/or the area numbed with a nerve block prior to trimming the nail above the break. Depending on the severity, a bandage may be placed to protect the injury. Antibiotics and pain medications may be prescribed if indicated. Broken nails are best prevented by keeping all nails short through regular trimmings.
Learn More -

Pneumothorax in Dogs
The definition of a pneumothorax is an accumulation of air outside the lungs, but inside the chest wall. The air outside the lung prevents the lungs from inflating normally, and can lead to lung collapse. There are several variations of pneumothorax.
Learn More -
Atrial Fibrillation in Cats
Atrial fibrillation describes very rapid contractions or twitching of the heart muscle, specifically in the atria. Most of the time, atrial fibrillation in cats occurs secondary to heart disease. Sometimes, in large breed cats, atrial fibrillation will occur as a primary heart problem. Most cats who develop atrial fibrillation have underlying heart disease, so the signs that are observed are often related to that underlying condition, and may include exercise intolerance, cough, or difficulty breathing. Treatment varies depending on whether the pet has primary or secondary atrial fibrillation. Your cat will need to be monitored on a regular basis.
Learn More -

Aortic Thromboembolism in Cats
An aortic thromboembolism results when a blood clot is dislodged and travels through the aorta, becoming lodged in a distant location. This causes severely reduced blood flow to the tissues receiving blood from that particular part of the aorta, leading to decreased oxygen in the tissues. Mixed breed cats, Abyssinian, Ragdoll, and Birmans are the most commonly affected. Sudden paralysis and pain, usually in the rear legs, are the most common clinical signs of aortic thromboembolism, although weakness and lameness may be seen. Other signs may include decreased or absent pulses in the femoral arteries of the rear legs, rapid breathing or difficulty breathing, vocalization from pain, vomiting, and the nailbeds and footpads may be pale or bluish. Initially, cats may need to be treated as inpatients. Drugs to prevent platelets from clumping together will be prescribed. The expected course of this disorder is days to weeks for full recovery of function to the legs, but the prognosis in general is very poor.
Learn More -

Acetaminophen Toxicity in Dogs
Acetaminophen, a common human drug used to control pain and fever, is toxic in dogs. Acetaminophen is occasionally recommended by veterinarians and should only be given under their direction. Young and small dogs have a higher risk for toxicity.
Learn More -
First Aid for Insect Stings in Cats
Insect stings or bites can cause mild signs of swelling, pain, and itching or can be more severe causing hives, anaphylactic reactions, difficulty breathing, vomiting, diarrhea, or seizures. If the bite or sting has been observed, look for the insect or spider to allow identification. Look for a stinger and remove it carefully without squeezing more venom out of the venom sac. Depending on the severity of the reaction, first aid including cool packing the area, dosing with oral antihistamine, and prevention of self-trauma may be all that is needed; however, in more severe cases emergency veterinary attention is required to stabilize the cat, screen for organ dysfunction, and provide supportive care.
Learn More -

Syncope (Fainting) in Dogs
Syncope (or fainting) is defined as a temporary loss of consciousness that occurs when the brain does not receive enough oxygen. Most dogs who experience syncope spontaneously recover once appropriate levels of oxygen reach the brain.
Learn More -

Onion, Garlic, Chive, and Leek Toxicity in Dogs
Besides making your dinner taste great, onions, garlic, leeks and chives can instigate severe medical problems for your dog. Although clinical signs of illness can occur soon after your dog eats the veggies, symptoms may take days to appear.
Learn More -
First Aid for Tail Injuries in Cats
Tail injuries are common and can sometimes be managed with home first aid but some cases require veterinary care. Abrasions are mild scrapes that can be treated with daily cleaning and application of antibiotic ointment. Lacerations are more serious cuts that may expose underlying muscle and bone requiring stitches and often antibiotics. Tail fractures can heal well if they occur near the tip of the tail but if bones are severely damaged then amputation may be required. Nerve damage can occur from fractures, crushing injuries or severe tail pulls causing stretching or tearing of the nerves and can result in loss of fecal and urinary continence and can also result in a limp tail.
Learn More -

Acetaminophen Toxicity in Cats
Acetaminophen is a medication that is used to treat fever and/or pain in humans. Cats have a genetic deficiency in a metabolic pathway in the liver that makes cats vulnerable to acetaminophen toxicity.
Learn More -
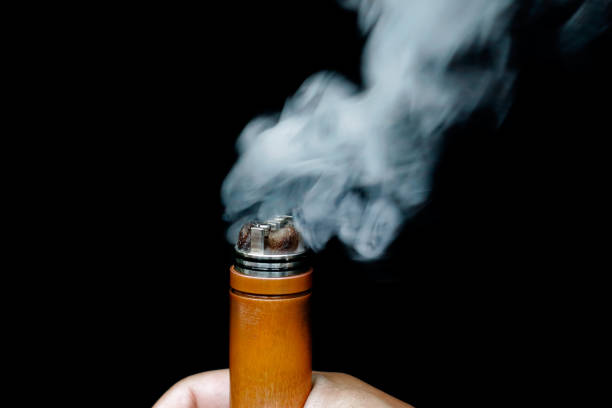

E-cigarettes and Pet Safety
Even though e-cigarettes may be safer for humans than using traditional tobacco products, they are certainly not safe for pets. The nicotine associated with e-cigarettes, even without the tobacco, poses a serious health threat for dogs and cats.
Learn More -
Pulmonary Thromboembolism (Blood Clots in the Lungs) in Cats
Pulmonary thromboembolism describes a condition when a blood clot lodges in one of the pulmonary arteries, blocking blood flow into the portion of the lung served by that artery. The signs of pulmonary thromboembolism include very sudden difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, decreased appetite, fainting, coughing, spitting up blood, weakness, exercise intolerance, and the inability to get comfortable. There are many important considerations and potential causes of pulmonary thromboembolism in cats. Many cats with thromboembolism are first treated as inpatients until the oxygen levels in their blood returns to normal. Once the cat returns home, it is important to restrict activity. There are some medications available for treating this disorder in cats. The prognosis for cats with pulmonary thromboembolism is generally guarded to poor, and it depends upon resolution of the underlying cause.
Learn More -
Taking Your Pet's Temperature
Normal body temperature for dogs and cats is 101 to 102.5°F (38.3 to 39.2°C). Pets with temperatures above 104°F (40.0°C) or falls below 99°F (37.2°C) need immediate veterinary care. Temperature can be taken rectally or aurally. If taking your pet’s temperature is too difficult, take your pet to your veterinarian. If your pet’s temperature remains high or low, take him to your veterinarian.
Learn More -

How Do Emergency Clinics Work?
If your pet had an emergency crisis, how would you manage it? Ask your veterinary hospital how they handle after-hour emergencies. Use this handout to help you plan ahead and be prepared in the event of a pet-health emergency.
Learn More -

Summer Toxins to Avoid with Your Pet
Summer is a great time to get outdoors and enjoy nature and the warm sunshine, especially with your pet. Pets are inquisitive creatures and love to investigate their surroundings. Unfortunately, this trait can lead pets down the path of injury and illness. The following information will help you to avoid many summer dangers that can affect your pet.
Learn More -
Cannabis (Marijuana) Intoxication in Cats and Dogs
Cats and dogs can become intoxicated by cannabis in various ways, most commonly by eating edibles (e.g., baked goods, candies, chocolate bars, and chips containing cannabis), or by ingesting cannabis directly (in any form). Pets can also be exposed to second-hand smoke. A small amount may affect one pet more than another, so there is no official safe level of exposure. Many of the signs of intoxication are neurological, including disorientation, dilated pupils, and hyperactivity. In severe cases, tremors, seizures, and coma can result. Regardless of the method of exposure, accurate and complete information from the owner is imperative to treat the patient successfully.
Learn More -

Sago Palm Poisoning
Sago Palms are pretty plants but beware—they pack a deadly punch for pets. The popular Sago Palm enhances outdoor landscapes in warmer areas of the U.S. and serves as indoor decor in many colder climates. All parts of the Sago Palm are poisonous, but the seeds (nuts) are the most toxic to pets. As with all poisoning cases, early detection and treatment increases the rate of success.
Learn More -
Cyanobacteria Poisoning
Blue-green algae, also called cyanobacteria, is found in fresh and brackish water of ponds and lakes. This microscopic bacteria can also grow in backyard fountains, garden pots, bird baths, and anywhere water is stagnant. Regardless of where they are found, cyanobacteria can be dangerous.
Learn More -
Porcupine Quills in Dogs and Their Dangers
Porcupines are the third largest rodent and live in many rural areas in North America. They are not aggressive, but they happily defend themselves, their offspring, and their dens if needed. Porcupine quills can puncture the skin and move through muscle, ultimately penetrating into body cavities and internal organs. Do not cut quills; cutting the shaft makes the quill splinter more easily which ultimately makes it harder to remove. Do not attempt to remove quills yourself. Seek immediate veterinary care if your dog is quilled. Sedation or anesthesia is required to remove quills safely. The best defense against porcupine quills is prevention. Avoid allowing the dogs to roam at dusk or after dark.
Learn More -
Vitamin D Poisoning in Dogs
Vitamin D poisoning occurs when a dog ingests a toxic dose of vitamin D. A common source of vitamin D poisoning is when a dog accidentally ingests rodenticides containing vitamin D. Another source of vitamin D poisoning is the accidental ingestion of certain human medications.
Learn More -
Vitamin D Poisoning in Cats
Vitamin D poisoning occurs when a cat ingests a toxic dose of vitamin D. A common source of vitamin D poisoning is when a cat accidentally ingests rodenticides containing vitamin D. Vitamin D poisoning causes a variety of clinical signs. The initial clinical signs, occurring anywhere from 8 to 48 hours after ingestion, include depression, weakness, and appetite loss. Vomiting, increased drinking and urination, constipation, and dehydration typically follow these signs.
Learn More -
Gastropexy
A gastropexy is a surgical procedure that is sometimes performed in large breed dogs to prevent the life-threatening condition, gastric dilatation and volvulus (GDV), also known as bloat. This handout explains how the procedure works, how it is used as a preventative and in emergency situations, risk factors, and post-operative care.
Learn More -

Anticoagulant Rodenticide Poisoning in Cats
Anticoagulant rodenticides are poisons used to kill mice, rats, and other rodents by preventing blood clotting. Poisoning occurs when a cat ingests rodenticide. Anticoagulant rodenticides cause excessive bleeding by interfering with vitamin K1 recycling in the body. Vitamin K1 is needed for the body to make certain clotting factors which enable blood to clot and help to control bleeding.
Learn More -

Anticoagulant Rodenticide Poisoning in Dogs
Anticoagulant rodenticide is used to kill mice, rats, and other pests. Poisoning occurs when a dog ingests rodenticide accidentally. Anticoagulant rodenticides causes excessive bleeding by interfering with vitamin K1 recycling in the body. Vitamin K1 is needed for the body to make certain clotting factors which enable blood to clot and help control bleeding.
Learn More -
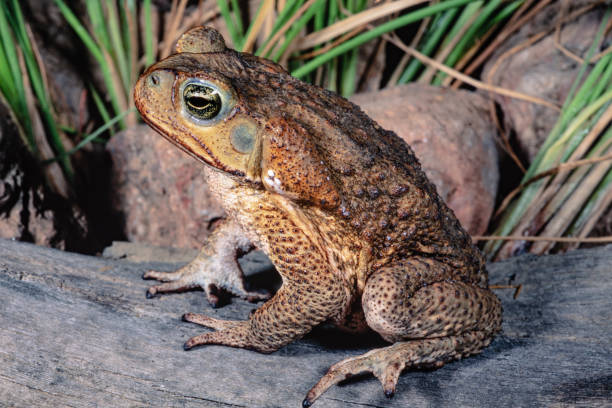

Toad Poisoning in Cats
Toad poisoning occurs when a cat is exposed to the toxins secreted by certain species of toads. The two most common species of toads that cause poisoning in the United States are the cane or marine toad and the Colorado River or Sonoran desert toad. While there are toads in Canada that secrete toxic substances, their effects are much less severe than the toxins secreted by the cane or Sonoran desert toads. Death can occur quickly and immediate treatment is required.
Learn More -
Ibuprofen Poisoning in Dogs
Ibuprofen is a commonly used NSAID and is used to treat fever, pain, and inflammation in humans. Ibuprofen poisoning occurs when a dog ingests a toxic dose of ibuprofen, either through misuse or by accident. Most commonly in dogs, clinical signs related to irritation and ulceration of the gastrointestinal tract are observed including decreased appetite, vomiting (sometimes with blood), diarrhea, depression, abdominal pain, dark tarry stools, and bloody stools.
Learn More -

Toad Poisoning in Dogs
Toad poisoning occurs when a dog is exposed to the toxins secreted by certain species of toads. The two most common species of toads that cause poisoning in the United States are the cane or marine toad and the Colorado River or Sonoran desert toad. While there are toads in Canada that secrete toxic substances, their effects are much less severe than the toxins secreted by the cane or Sonoran desert toads. Death can occur quickly and immediate treatment is required.
Learn More -
Aspirin Poisoning in Dogs
Aspirin is a commonly used over the counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and is used to treat fever, pain, inflammation (swelling), and clotting disorders in humans. Aspirin poisoning occurs when a dog ingests a toxic dose of aspirin, either through misuse or accidentally. he most common side effect of aspirin is gastrointestinal irritation, which can lead to signs such as a decreased appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Treatment for aspirin poisoning depends on how quickly the dog is seen by the veterinarian.
Learn More -
Aspirin Poisoning in Cats
Aspirin is a commonly used over the counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and is used to treat fever, pain, inflammation (swelling), and clotting disorders in humans. Aspirin poisoning occurs when a cat ingests a toxic dose of aspirin, either through misuse or accidentally. Clinical signs depend on how much aspirin was eaten. Treatment for aspirin poisoning depends on how quickly the cat is seen by the veterinarian.
Learn More -
Arsenic Poisoning in Dogs
Arsenic poisoning is the accidental ingestion, skin contact, or inhalation of products containing a toxic dose of arsenic. Clinical signs can include abdominal pain, salivation, vomiting, diarrhea, staggering, weakness, rapid weak pulse, lethargy, low body temperature, collapse, and death. Supportive therapy is a crucial part of treating arsenic poisoning.
Learn More -
Botulism in Dogs
Dogs are exposed to botulism by eating raw meat or dead animals containing botulinum toxin produced by Clostridium botulinum. Botulism causes ascending paralysis of the nervous system. Clinical signs are reviewed as well as diagnostic tests and treatment. Prognosis is guarded depending on the amount of toxin ingested and the degree of supportive care available. There is no vaccine.
Learn More -
Botulism in Cats
Cats are exposed to botulism by eating raw meat or dead animals containing botulinum toxin produced by Clostridium botulinum. Botulism causes ascending paralysis of the nervous system. Clinical signs are reviewed as well as diagnostic tests and treatment. Prognosis is guarded depending on the amount of toxin ingested and the degree of supportive care available. There is no vaccine.
Learn More -

Blood Transfusion Reactions in Cats
A transfusion reaction is a medical reaction that occurs in response to a blood transfusion. Many transfusion reactions occur acutely, within seconds of starting the transfusion up to 48 hours post-transfusion. In other cases, however, transfusion reactions may be delayed. In many cases, a transfusion reaction can be diagnosed based on clinical signs alone. Your veterinarian will then administer medications specific to the type of reaction that your cat is experiencing.
Learn More -

Blood Transfusion Reactions in Dogs
A transfusion reaction is a medical reaction that occurs in response to a blood transfusion. Many transfusion reactions occur acutely, within seconds of starting the transfusion up to 48 hours post-transfusion. In other cases, however, transfusion reactions may be delayed. In many cases, a transfusion reaction can be diagnosed based on clinical signs alone. Your veterinarian will then administer medications specific to the type of reaction that your dog is experiencing.
Learn More -

Metaldehyde Toxicity (Slug Bait Poisoning)
Metaldehyde toxicity occurs when a dog (or, less commonly, a cat) eats slug bait that contains metaldehyde. The signs of metaldehyde toxicity include vomiting, anxiety, ataxia (due to muscle incoordination), stiffness, muscle tremors, elevated heart rate and respiratory rate, increased salivation, and increased sensitivity to touch. These signs often progress to continuous muscle tremors and seizures. Diagnosis is based on clinical signs and history. There is no antidote to metaldehyde; treatment is centered upon decontamination and supportive care. Prognosis is good, with aggressive treatment.
Learn More -
Pleural Effusion in Dogs
Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity. The fluid is not found within the lungs, but instead within the pleural sac, essentially meaning the lungs are floating in a chest that is full of fluid. There are several causes, including chylothorax, heart failure, and lung or chest tumors. Dogs presenting for pleural effusion are often experiencing shortness of breath and decreased oxygen intake; placing them into an oxygen cage provides some degree of immediate relief. Removing the fluid that surrounds the lungs will allow the dog to breathe more readily and this fluid can then be tested to identify the cause of the pleural effusion. The treatment and prognosis vary depending on the underlying cause.
Learn More -

Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Shock Lung) in Dogs
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening complication of critical illness. These underlying critical illnesses may include sepsis, pancreatitis, pneumonia (either due to an infection or the inhalation of foreign materials), trauma, near-drowning, and other severe illnesses. In ARDS, massive inflammation and the release of various inflammatory chemicals leads to the leaking of capillaries within the lungs. Signs of ARDS include increased respiratory rate, blue discoloration to skin and mucous membranes due to poor oxygen delivery, and occasionally coughing. Treatment of ARDS is primarily focused on supportive care and addressing the underlying critical illness.
Learn More -

Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Shock Lung) in Cats
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening complication of critical illness. These underlying critical illnesses may include sepsis, pancreatitis, pneumonia (either due to an infection or the inhalation of foreign materials), trauma, near-drowning, and other severe illnesses. In ARDS, massive inflammation and the release of various inflammatory chemicals leads to the leaking of capillaries within the lungs. Signs of ARDS include increased respiratory rate, blue discoloration to skin and mucous membranes due to poor oxygen delivery, and occasionally coughing. Treatment of ARDS is primarily focused on supportive care and addressing the underlying critical illness.
Learn More -

Pyothorax in Dogs
Pyothorax occurs when pus or inflammatory fluids collect in the space around the lungs causing fever, anorexia, lethargy, and difficulty breathing. It is diagnosed through history, physical exam, radiographs, and thoracocentesis. Treatment with oral antibiotics is essential and may involve repeated thoracocentesis or the placement of a chest drain.
Learn More -

Pericardial Effusion in Cats
Pericardial effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the sac surrounding the heart. Pericardial effusion can have a number of underlying causes, including inflammation, infection, cancer, and hereditary defects. Mild cases of pericardial effusion may be asymptomatic, but more significant fluid accumulations can interfere with the heart’s function and lead to severe effects such as sudden death. Treatment and prognosis is dependent upon the underlying cause of the condition.
Learn More -

Smoke Inhalation in Dogs
Smoke inhalation injuries are caused by a combination of heat and airborne toxins. Clinical signs of smoke inhalation vary, depending on the materials contained within the smoke and how much smoke the dog inhales. Common signs include coughing, shortness of breath, eye injuries, and burns. Neurologic signs can also occur, especially in cases of carbon monoxide inhalation. Treatment typically involves oxygen therapy and other supportive care measures.
Learn More -

Smoke Inhalation in Cats
Smoke inhalation injuries are caused by a combination of heat and airborne toxins. Clinical signs of smoke inhalation vary, depending on the materials contained within the smoke and how much smoke the cat inhales. Common signs include coughing, shortness of breath, eye injuries, and burns. Neurologic signs can also occur, especially in cases of carbon monoxide inhalation. Treatment typically involves oxygen therapy and other supportive care measures.
Learn More -

Meningitis in Cats
Meningitis refers to inflammation of the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Causes include bacterial infection, viral infection, fungal infection, protozoal infection, aberrant parasite migration, or immune-mediated disease. A CSF tap is the most accurate way to diagnose meningitis, though CT and MRI may also be beneficial. Treatment and prognosis vary, depending upon the underlying cause.
Learn More -
Meningitis in Dogs
This handout discusses meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord, in dogs. The numerous potential causes, along with the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of the condition are outlined.
Learn More -

Mushroom Toxicity
Mushroom toxicity can run the gamut from irritating illness to severe toxicity to death. The species of mushroom and amount ingested determine the severity of the toxicity. Since mushrooms are difficult to identify, it is best to discourage your pet from eating any mushrooms growing in the wild. In the event of mushroom ingestion, prompt treatment is critical to successful treatment. Pet owners need to be alert to the possibility of mushroom toxicity and work to eliminate their pet’s access to mushrooms.
Learn More -

Strokes in Cats
Strokes are rare in cats. Some causes include a blood clot such as a thrombus or embolus that lodges in a cerebral blood vessel, or cerebral bleeding from trauma or as a result of thrombocytopenia; however, the cause is often unknown. Signs of a stroke are variable depending on the region or regions of the brain affected, and the degree and duration of blood and oxygen deprivation. Magnetic resonance imaging is the ideal diagnostic test for diagnosing a stroke. Treatment is quite complex and there is no guarantee of complete success. Your veterinarian will help you assess progress and plan remedial action.
Learn More -

Hypokalemia (Low Potassium Levels) in Dogs
Hypokalemia is a term that refers to a low blood concentration of potassium. Potassium is an important electrolyte within the body and is vital for the normal function of muscles and nerves. Mild to moderate hypokalemia often does not cause clinical sigs, but severe hypokalemia can result in generalized muscle weakness, lack of appetite, and some dogs may become constipated. The underlying cause of hypokalemia is often chronic kidney failure. Hypokalemia and its associated clinical signs may be quickly corrected by potassium supplementation. Depending on the cause, it may be necessary to continue supplementing potassium permanently.
Learn More -

Shar-Pei Recurrent Fever Syndrome
Shar-Pei recurrent fever syndrome is a hereditary condition that affects nearly one in four Shar-Pei dogs. Affected dogs experience recurrent episodes of fever and inflammation, with no identifiable underlying cause. Inflammatory cytokines released during fever episodes contribute to the production of a protein called amyloid which is then deposited in a variety of internal organs, resulting in a condition known as amyloidosis. Signs that may accompany the fever episodes include swelling of the hocks and muzzle, abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often prescribed to reduce fever and alleviate discomfort. Colchicine is the drug of choice for the long-term treatment. Affected dogs can often be managed, but the condition will affect them for the remainder of their lives. If your dog is already showing signs of chronic kidney disease, your veterinarian will also develop a treatment plan to address the kidney disease.
Learn More

